Within the realm of process improvement and quality management, organizations often turn to structured methodologies to navigate the complexities of enhancing operational efficiency and satisfying customer needs. Two such methodologies, DMAIC and DMEDI, stand out as pillars of Six Sigma philosophy, each offering distinct approaches tailored to specific objectives. In this blog post, we embark on a comprehensive exploration of DMAIC and DMEDI, dissecting their fundamental principles, delineating their applications across industries, and elucidating the key differentiators that set them apart. By unraveling the intricacies of these methodologies, organizations can gain invaluable insights into optimizing processes, driving innovation, and fostering enduring customer satisfaction in today’s fiercely competitive landscape.
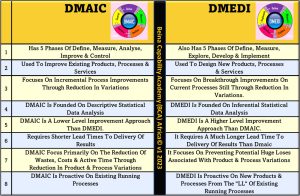
Six Sigma DMAIC is usually used as a fix for internal organizational issues and problems. However, the true benefit of Six Sigma is felt when the organization moves from fixing broken processes to the Design for Six Sigma (DFSS). DFSS methodology is aimed at building processes properly from the outset. The DMEDI is one such DFSS roadmap methodologies for designing or redesigning processes. This (re)design normally comes into use in the advanced stages of SS implementation in an organization.
DMAIC: Enhancing Existing Processes
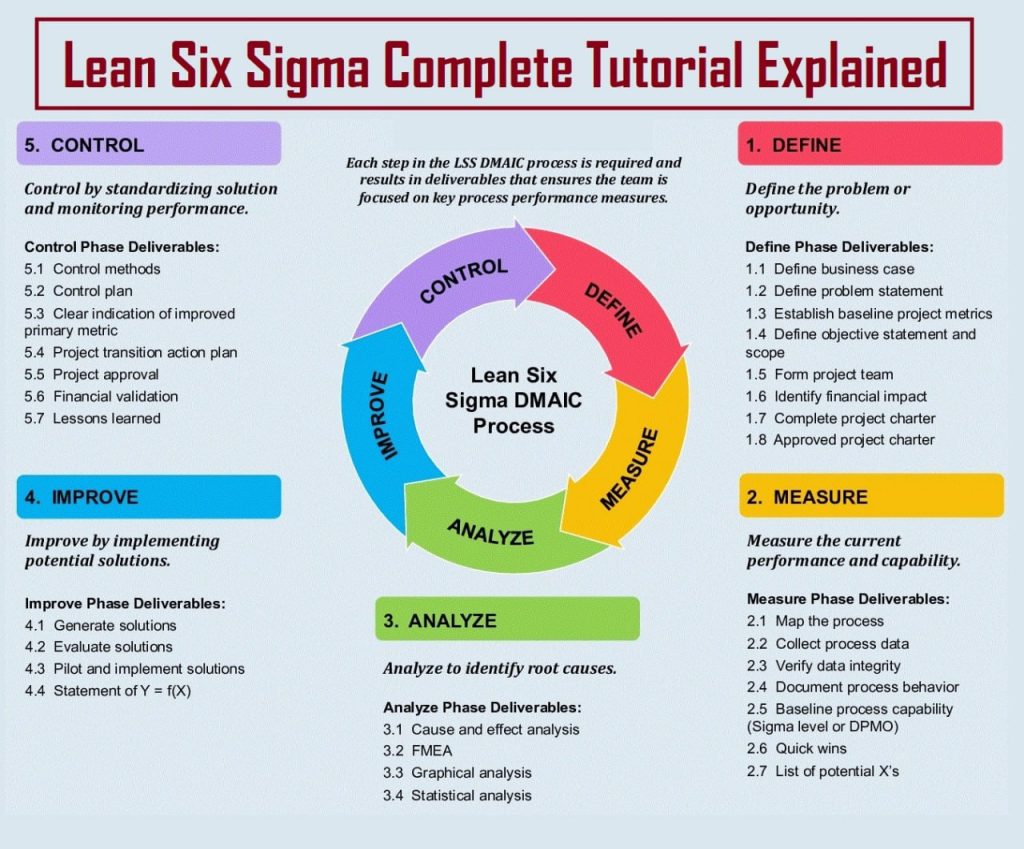
DMAIC, an acronym for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, represents a systematic framework aimed at improving existing processes within an organization.
- Define: The DMAIC journey commences with a meticulous definition of the problem at hand, project goals, and the precise requirements of the end-user. Establishing a clear understanding of the scope lays the foundation for subsequent phases.
- Measure: Rigorous measurement and data collection characterize this phase, providing organizations with a comprehensive understanding of the current state of their processes. By establishing a baseline performance level, DMAIC enables objective assessment and targeted improvement efforts.
- Analyze: Root cause analysis takes center stage in this phase as organizations delve deep into data to unearth the underlying factors contributing to inefficiencies or defects. Through statistical analysis and qualitative assessment, DMAIC facilitates informed decision-making.
- Improve: Armed with insights gleaned from the analysis phase, organizations embark on developing and implementing solutions to optimize process performance. Continuous iteration and refinement ensure that proposed improvements align with organizational goals and customer expectations.
- Control: To safeguard against regression and sustain the gains achieved through improvement efforts, DMAIC emphasizes the implementation of robust control mechanisms. Ongoing monitoring, feedback loops, and process standardization contribute to the long-term viability and effectiveness of implemented solutions.
DMEDI: Designing New Solutions
DMEDI, encapsulating Define, Measure, Explore, Develop, and Implement, offers a structured approach tailored for designing and implementing novel processes or solutions within organizations.
- Define: Similar to DMAIC, the DMEDI journey begins with a comprehensive definition of project goals, customer requirements, and the scope of the endeavor. Establishing a solid foundation ensures clarity of purpose and direction throughout the design process.
- Measure: In DMEDI, measurement extends beyond assessing current process performance to encompass gathering data on customer needs, preferences, and expectations. This holistic understanding serves as a cornerstone for crafting solutions that resonate with end-users.
- Explore: A distinguishing feature of DMEDI, the Explore phase fosters creativity and innovation by encouraging the exploration of alternative solutions and design concepts. Organizations leverage brainstorming sessions, prototyping, and scenario analysis to unearth optimal approaches.
- Develop: With a preferred solution identified, the Develop phase entails detailed planning encompassing design, testing, and validation. Iterative refinement ensures that the chosen solution is not only technically feasible but also aligns with organizational objectives and customer needs.
- Implement: The culmination of the DMEDI process, the Implement phase involves deploying the solution into the operational environment. Close monitoring and feedback mechanisms facilitate adjustments as necessary, ensuring seamless integration and optimal performance of the newly designed solution.
SIMILARITIES: Shared Foundations of Success
Despite their distinct objectives, DMAIC and DMEDI share several fundamental similarities that underpin their effectiveness in driving organizational excellence:
- Structured approach: Both methodologies adhere to a structured, phased approach, providing organizations with a clear roadmap for navigating the complexities of process improvement and solution design. By breaking down the improvement journey into manageable stages, DMAIC and DMEDI instill discipline and clarity, fostering systematic progress towards organizational goals.
- Customer focus: At the heart of both methodologies lies a steadfast commitment to understanding and meeting customer needs. Whether it’s optimizing existing processes or designing new solutions, DMAIC and DMEDI prioritize customer requirements, ensuring that improvement efforts are aligned with enhancing customer satisfaction and driving value creation.
- Data-driven decision-making: Central to the success of DMAIC and DMEDI is their reliance on data and statistical analysis. By leveraging empirical evidence, organizations gain valuable insights into process performance, root causes of issues, and customer preferences. This data-driven approach not only enhances the accuracy of decision-making but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
These shared foundations underscore the versatility and applicability of DMAIC and DMEDI across diverse industries and organizational contexts, serving as catalysts for driving sustainable success and competitive advantage.
DIFFERENCES: Divergent Paths to Excellence
While DMAIC and DMEDI share common principles, they diverge in key aspects, reflecting their distinct objectives and applications:
- Purpose: The primary divergence between DMAIC and DMEDI lies in their overarching goals. DMAIC focuses on improving existing processes by identifying and rectifying inefficiencies or defects, aiming for incremental enhancements in performance and quality. In contrast, DMEDI is geared towards designing new processes or solutions from scratch, catering to situations where innovation and novel approaches are required to address evolving customer needs or market demands.
- Exploration phase: A notable point of departure between DMAIC and DMEDI is the inclusion of an “Explore” phase in the latter. While DMAIC follows a linear progression from problem definition to solution implementation, DMEDI incorporates a dedicated phase for exploring alternative solutions and design concepts. This emphasis on creativity and innovation distinguishes DMEDI, providing organizations with the freedom to consider diverse approaches before committing to a particular solution.
- Implementation timing: Another key distinction between DMAIC and DMEDI lies in their optimal timing for implementation. DMAIC is typically deployed in scenarios where incremental improvements within existing processes are sought, making it well-suited for organizations aiming to fine-tune their operations and achieve marginal gains over time. On the other hand, DMEDI finds its niche in early-stage design endeavors, catering to situations where radical innovation or transformative change is required to address emerging challenges or seize new opportunities.
By recognizing and understanding these differences, organizations can tailor their approach to process improvement and solution design, selecting the methodology best suited to their specific objectives and contextual requirements. Whether pursuing incremental enhancements or embarking on a journey of innovation, DMAIC and DMEDI offer distinct paths to excellence, empowering organizations to drive sustained success and competitive advantage in dynamic and evolving markets.